Google Analytics is a powerful tool that helps website owners understand how visitors interact with their site. One of the key features in Google Analytics is the concept of dimensions and metrics. In this article, we will explore the “secondary dimension” in Google Analytics, a feature that allows users to view their data in a more detailed and insightful way.
What is a “Secondary Dimension”?
A secondary dimension in Google Analytics is an additional parameter that you can add to your data analysis to see more detailed information about your visitors’ activity on your website or app. Secondary dimensions create subsets of data to find nuances.
For example, you could use a secondary dimension to see how new users from different countries interact with your website differently than returning users. Here’s how it works:
Understanding Dimensions and Metrics
- Dimensions: These are attributes of your data, like the city from which a session originates or the URL of a page that is viewed.
- Metrics: These are quantitative measurements, like the total number of sessions or the average number of pages viewed per session.
Examples of Secondary Dimensions in Google Analytics

Here are some examples of secondary dimensions that you can use in Google Analytics:
- Country – Visitors from different countries can use this dimension to observe how they interact with your website.
- City – Visitors from various cities can utilize this dimension to analyze how they engage with your website.
- Device – Visitors using different devices can employ this dimension to assess how they interact with your website.
- Browser – Visitors using different browsers can apply this dimension to evaluate how they interact with your website.
- Source/Medium – You can use this dimension to observe how visitors arrived at your website.
Example Table:
| City | Browser | Sessions | Pages/Session |
| San Francisco | Chrome | 3,000 | 3.5 |
| San Francisco | Firefox | 2,000 | 4.1 |
| Berlin | Chrome | 2,000 | 5.5 |
| Berlin | Safari | 1,000 | 2.5 |
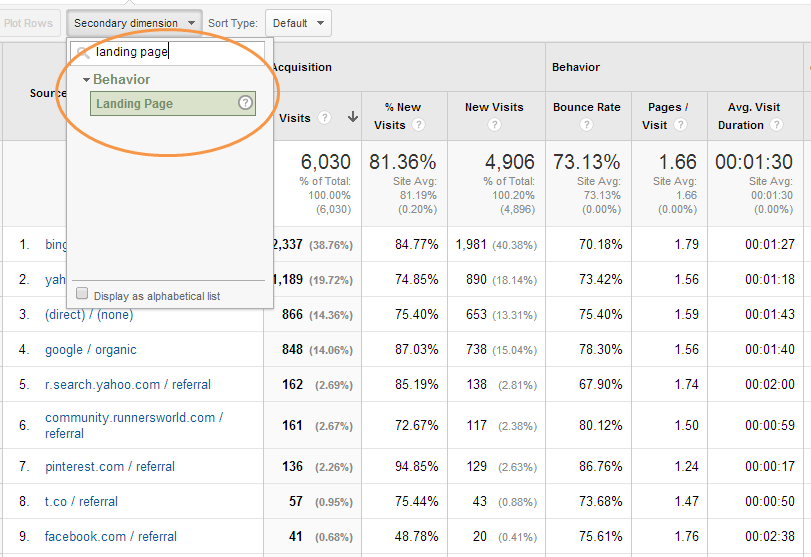
How to Add a Secondary Dimension in Google Analytics?
To add a secondary dimension to a report in Google Analytics, follow these steps:
- Go to the Reports tab in Google Analytics.
- Select a report that you want to add a secondary dimension to.
- Click the Secondary dimension drop-down menu.
- Select the dimension that you want to add.
- Click the Apply button.
Why Use a Secondary Dimension in Google Analytics?
Using a secondary dimension can provide deeper insights into user behavior. Here are some benefits:
- More Detailed Analysis: It allows you to simultaneously analyze data with two dimensions.
- Customized Reporting: You can combine different dimensions and metrics that share the same scope.
- Better Decision Making: The additional insights help in making informed decisions.
Valid Dimension-Metric Combinations
Not every metric can be combined with every dimension. They must share the same scope, such as user level, session-level, or hit level. Google Analytics provides a reference for valid dimension-metric pairs.
How Metrics are Calculated
Metrics in Google Analytics are calculated in two ways:
- Overview Totals: Summary statistics for the entire site.
- Reporting Dimensions: Metric value qualified by selected dimensions.
Attribution Models
Google Analytics uses different attribution models to answer various questions about user behaviour. These include:
- Per Request Attribution: Aggregate values for a single metric or dimension pairing.
- Page Value Attribution: Answers how useful a page was in relation to a goal or revenue value.
- Site Search Attribution: Displays goal conversion rates and values per search term.
Also Read: Elon Musk Launches New Payout Program
The “secondary dimension” in Google Analytics is a powerful feature that allows for a more detailed and customized analysis of data. By understanding and utilizing this feature, website owners and marketers can gain deeper insights into user behavior, optimize their strategies, and make more informed decisions.

